The Role Of The Gut Microbiota In Autism

Although autism is associated with neurological disorders, the gut microbiota is often different as well. In fact, most autistic people suffer from gastrointestinal problems. They also often involve changes in the immune system. With this in mind, in the next article we will look at how the gut flora is related to this condition.
The gut microbiota
The composition of the gut microbiota is different in the stomach, small intestine and large intestine. The thousands of microbial species, bacteria, viruses and a number of fungi that live there are therefore the main protective system of the gastrointestinal tract.
The microbiota is involved in the correct functioning of the organism in several ways. Think of various things such as:
- Establishing an intestinal barrier that controls the passage of various substances, preventing pathogenic species from passing through the intestinal wall.
- Allowing the immune system to mature, thus boosting innate and acquired immunity.
- And finally, the management of the synthesis and metabolism of nutrients, hormones and vitamins, as well as the elimination of toxic substances.
Changes in the bacterial composition of these microbiota are caused by various factors such as diet, antibiotic use, lifestyle and genetics. However, people with autism have a different gut microbiota composition than other people.
Recent studies also suggest that there could be a link between changes in the flora and a number of psychiatric disorders such as autism, schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease.
The connection between brain and gut
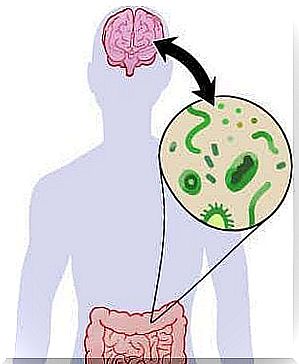
Dysbiosis is the change in the bacterial composition of the gut that leads to the production and distribution of lipopolysaccharide (LSP) in the blood. This is a pro-inflammatory endotoxin and affects the modulation of the central nervous system and controls emotions.
There is a bidirectional connection between the central nervous system and the gut. Neurons can alter the microbial composition of the gut flora and alter gut permeability. In this way, the brain directly influences the gut microbiota.
At the same time, publications show that these microbiota direct the activities of the central nervous system. A study in the journal Brain, Behavior and Immunity examined how Campylobacter jejuni bacteria increased anxiety levels in mice.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
This condition involves a series of neurological changes characterized by restricted and repetitive behavior, as well as deficits in social interaction and communication.
People with autism are often treated with antibiotics to treat other underlying diseases such as a chronic middle ear infection. This affects the protective gut microbiota and facilitates the colonization of neurotoxin-producing bacteria.
In addition, many children with autism suffer from gastrointestinal problems, such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which causes the following symptoms in children who suffer from it:
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Stomach ache
- Vomit
- Sleep problems
- Irritability
Microorganisms of the gut microbiota in autism
Clostridium
Clostridia bacteria are present at a higher concentration in patients with ASD. While many of these bacteria are beneficial and part of healthy gut flora, there are pathogenic species, such as C. tetani and C. perfrigens, that produce toxins and cause serious illness in humans.
In a study published in the Journal of Child Neurology , most children with regressive autism who received vancomycin treatment showed improvements in gastrointestinal and neurobehavioral symptoms. This points to the influence of the microbiota in autism and its possible modification.
sutterella
Researchers have also found this bacterium in biopsies taken from the gastrointestinal mucosa and feces of children with ASD. Since it is hardly present in non-autistic people, experts consider Sutterella to be the most important part of the microbiota in people with autism.
Desulfovibrio, Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium
Finally, experts have linked Desulfovibrio species to the most severe symptoms of autism. These bacterial species produce propionic acid. This appears to be related to the pathogenesis of ASD.
- Lactobacilli are also present in a higher concentration in patients with ASD.
- Bifidobacteria are also present in smaller quantities than normal.
Treatments for changes in the gut microbiota in autism

Since the microbiota appears to play an important role in the pathophysiology of ASD, treatments are based on modifications of the bacterial composition. The goal is to restore balance so as not to alter the nervous system. In this regard, some of the treatment options tested include:
- Probiotics: Probiotics have the ability to normalize the microbiota and gut problems. It is useful as an alternative for treating gastrointestinal symptoms and autism.
- Faecal microbiota transplantation: This procedure transfers the fecal microbiota from a healthy person to a patient suffering from dysbiosis. It has been helpful in treating cases of inflammatory bowel disease. It has also helped to improve the symptoms of constipation.
- Diet: People with autism often have problems eating. These people may eat less fruits and vegetables, but also less protein. Improving their diet could therefore help the health of their gut flora.
- Antibiotics: These substances cause changes in the microbiota. Specific drugs such as vancomycin or minocycline have been tested.
Microbiota in autism: an area of research
There appears to be substantial scientific evidence for the influence of the gut microbiota in people with autism. In any case, it is essential to continue research for more certainty. If you have a family member with autism, it is best to consult specialists in the field to choose the best treatment approach.