The Characteristics And Treatment Of Salivation
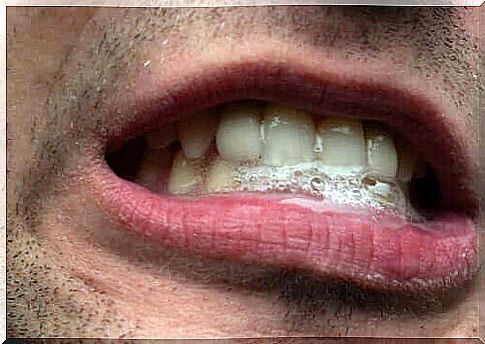
Sialorrhea or salivation is what we call ‘drooling’ in common language. This condition is, of course, very common in children between the ages of 15 and 36 months. However, it is considered abnormal if it occurs after the age of four. Today we are going to take a closer look at the characteristics and treatment of salivation.
Although salivation appears to be a condition that only affects appearance, it can also be associated with serious health problems. These include, for example, cerebral palsy or Parkinson’s disease. It can also be the result of pregnancy or taking certain medications.
What is salivation and what causes it?
Salivation is a condition characterized by the inability to retain saliva in the mouth and direct it to the digestive tract. It is an excessive production of saliva or an abnormality in its processing.
The most common causes of salivation are neurological disorders (Spanish link). Among them, as we mentioned, are cerebral palsy and Parkinson’s disease. However, it also occurs in people who have amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Riley-Day syndrome, or the effects of a stroke.
This condition is also common among those taking antipsychotic, hypnotic, or sedative medications. Likewise, it is common for a sudden increase in saliva production during pregnancy to occur between the second and fourth week of pregnancy.
The characteristics of this condition
The salivary glands are responsible for saliva production. There are three of them: the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands. The first produces watery saliva, while the other two continuously produce a thicker fluid. This is the type of saliva that often leads to choking.
Every day they produce about 50 grams of saliva, 70% of which comes from the submandibular and sublingual glands (link in spanish). As such, salivation is not a disease that evolves into another, more serious condition. However, it has serious consequences for a person’s quality of life.
There is no specific doctor who specializes in the treatment of salivation. You should therefore consult your doctor if you suspect this condition. He or she will refer you to a specialist depending on the cause of the problem.
Classification of salivation
From the point of view of the origin of salivation , two types of salivation have been described. These can then be divided into the following two:
- Anterior sialorrhea : arises from a neuromuscular deficiency in combination with excessive saliva production. It leads to the liquid spilling from the corners of the mouth or the lower lip.
- Posterior sialorrhea: When the problem arises in the flow of saliva from the tongue to the pharynx.
According to the Thomas-Stonell and Greenberg rating scale (Spanish link), it is also possible to classify salivation based on severity or frequency. From that point of view, the graduation is as follows:
- Dry mouth
- Mild (wet lips)
- Moderate (wet lips and chin)
- Severe (wet clothes)
- Abundant (clothes, hands and utensils are wet)
Depending on the frequency of salivation, the Thomas-Stonell and Greenberg rating scale can be divided as follows:
- never drool
- Drool every now and then
- Frequent sialorrhea
- Constant drooling
Consequences of salivation

Salivation is a relevant medical problem. It not only causes a noticeable disability (Spanish link), but also additional difficulties in the treatment of patients with neurological problems. In general, this condition has consequences. These may include the following:
- flaky lips
- muscle fatigue
- Dermatitis
- Changes in the sense of taste
- Difficulties with the voice
However, from a physical point of view, the greatest risk is aspiration pneumonia (Spanish link), due to difficulty swallowing food. These patients are also more prone to oral infections.
At the same time, the psychosocial consequences can be very serious. Drooling leads to social rejection, even among caregivers. This also limits the normal performance of daily activities.
The treatment of salivation
There are three ways to treat salivation: speech therapy, pharmacology, and surgery. The speech therapy approach involves performing a series of exercises to inhibit the pathological reflexes.
Specifically, the goal of this saliva treatment is to improve the closing of the lips and the aspiration or ingestion of saliva. Continuous training can lead to improvement.
As for the pharmacological treatment, it concerns anticholinergics, which help to reduce the secretion of saliva. However, these drugs should go hand-in-hand with exercise. Unfortunately, some people experience an intolerance to this type of medication.
It is also possible to treat salivation by injection of botulinum toxin type A (TBA). This is applied directly to the salivary glands and also reduces the production of saliva. The most positive is that it causes very few side effects (Spanish link).
Finally, if none of these measures work, the specialist will likely decide to perform a surgical procedure. Every patient is different and sometimes a combination of measures is needed to achieve effectiveness.