Medication Used In Intubation
Compromised airways and breathing are one of the leading causes of death and serious morbidity in adults and the elderly. Therefore, cardiopulmonary resuscitation techniques, such as intubation, are one of the most important options when dealing with these types of emergencies.
There are some obstacles to the procedure arising from the anatomy of the laryngeal structures, the limited time to resolve the problem, and the poor visibility of the structures. That’s why medical professionals use certain medications that help them intubate patients more easily.
What is an intubation?
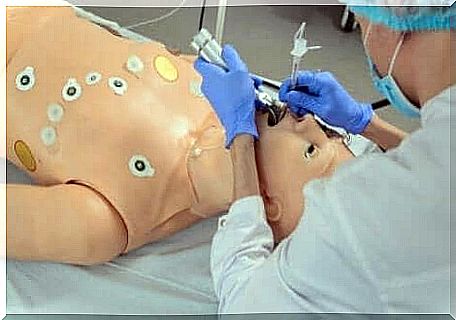
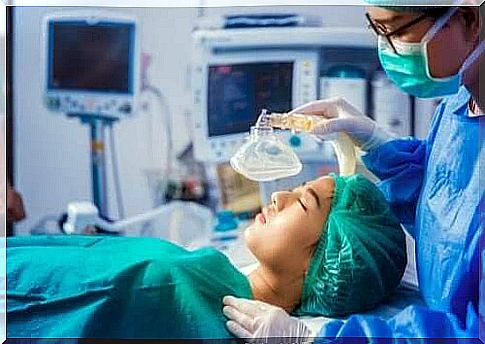
An intubation consists of quickly inserting a tube into the trachea to provide a good passageway for air. Once doctors have inserted the tube, they can secure the patient’s breathing. Intubation is the preferred method of controlling a patient’s airway because of the benefits it provides.
- Its main benefit is that it holds up the airway, allowing air to flow in and out with ease.
- It also prevents stomach problems in certain cases, which are caused by the stomach filling with air.
- In addition, it helps to enable deep tracheal breathing and ensures that the patient receives a higher oxygen concentration in the blood.
- This procedure also eliminates the need for a tight-fitting face mask.
When does the doctor choose an intubation?
There are precise guidelines as to when this procedure should be performed. The most common situation is when the patient has a cardiac arrest. However, there are other situations that require intubation such as:
- patients in whom, for example, their airways need to be protected or kept open.
- people who have suffered traumatic brain injuries with a Glasgow scale of less than 8 points.
- people with respiratory failure of more than 30 or less than 10 breaths per minute.
- In addition, doctors may intubate someone who has impending respiratory failure or airway edema, for example, due to burns or anaphylaxis.
Commonly used medication during intubation
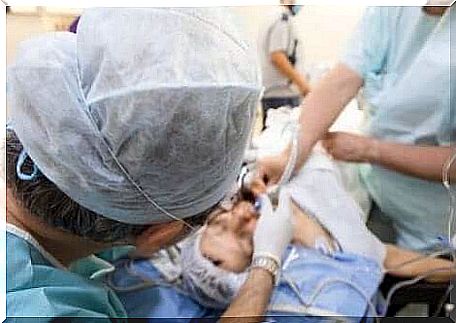
To facilitate insertion of the intubation tube, doctors often use certain medications. During intubation, the body produces a powerful adrenergic shock response that manifests itself in problems such as:
- tachycardia
- hypertension
- increased ocular and intracranial pressure
Therefore, at a stage called preoxygenation, the following drugs are often administered to reduce this physiological response:
- Lidocaine : Doctors use this for patients with intracranial hypertension or increased bronchial reactivity. The recommended dose of lidocaine is 1.5 mg/kg of weight, ideally administered 3 minutes before performing an intubation.
- Fentanyl : This is an opioid that reduces the response of the sympathetic nervous system. That is, it counteracts tachycardia and arterial hypotension. It is important to be very careful when taking this drug as it can cause breathing problems.
- Atropine : Doctors use this to prevent bradycardia in pediatric patients.
- A neuromuscular blocker : Its use is not currently recommended as doctors are not aware of its actual benefit in terms of reducing muscle twitching . However, they do know the adverse effects of these types of drugs.
Other medications used
As for the induction and paralysis phase, physicians administer sedatives leading to unconsciousness and then a neuromuscular relaxant, usually succinylcholine. The most common clinically used neuromuscular blocking and inducing agents include:
- Etomidate : This is the most commonly used drug for inducing hypnosis. It does not affect hemodynamics.
- Ketamine : This is the only drug with hemodynamic stability comparable to etomidate. It’s a dissociative anesthetic. It triggers catecholamine release, which increases heart rate, blood pressure, and cardiac output. It is ideal for patients with hypotension.
- Barbiturates : Thiopental, like propofol, is commonly used in anesthesia. It is recommended for patients with suspected intracranial hypertension who are hemodynamically stable.
- Benzodiazepines : Midazolam is the most commonly used drug in this category. It acts relatively quickly and has a short duration of action compared to other drugs in the same family. In addition, it gives a stronger loss of memory.