Everything You Need To Know About Bone Marrow Edema

Bone marrow edema is an inflammatory process that usually occurs in the trabecular bone. In other words, it occurs in the internal spongy component of the bones.
The causes range from trauma to degenerative diseases. It also sometimes occurs in those who begin to engage in strenuous physical activity after leading a sedentary life.
The scientific journal Dolor, Investigación, Clínica y Terapéutica (Spanish link) explains that this pathology is common in the clinical practice of rheumatology.
This is because there is greater use and availability of magnetic resonances as a diagnostic test. This makes it easier to identify these kinds of problems. With all that in mind, what are its features?
What is bone marrow edema?
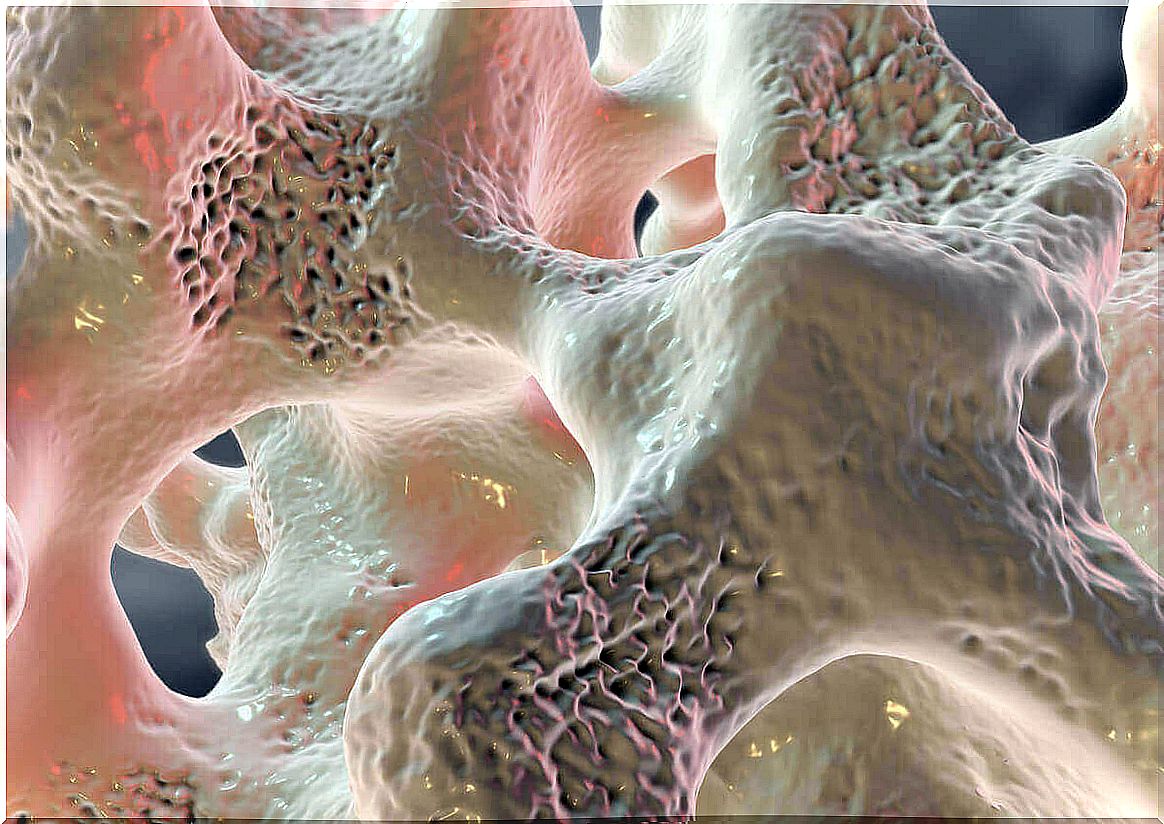
Simply put, we can say that bones consist of two parts that are easy to distinguish. One is the cortical bone, which is made of a hard and compact material that surrounds the outer layer of the skeleton. The other is the trabecular bone, a more spongy tissue that makes up the internal skeletal fabric.
The trabecular bone contains a large number of blood vessels, because the bones also need to be nourished. According to an article published by the FASTA University of Argentina (Spanish link), a buildup of fluid in the trabecular bone causes bone inflammation.
This is common because the blood vessels break and bleeding into the bone occurs. The cause may also lie in the accumulation of inflammatory fluid after an injury. In any case, you could say that bone marrow edema is a kind of bruise in the bone.
However, it is important to understand that this condition can also occur in the cortical bone, even if it is not very common. Similarly, it is important to note that its characteristics vary depending on the reversibility. So, experts classify it into two large groups:
- Transient bone edema syndrome (TBES): This is a reversible inflammatory process that subsides with treatment and over time.
- Osteonecrosis: This causes the death of bone-forming cells (osteocytes). For this reason, experts consider it an irreversible condition.
Why does bone marrow edema occur?
As you might expect, most bone marrow edema is the result of injury, falls, high physical strain, or overexertion. Nevertheless, Reumatologia del Hospital General de Elche (Spanish link) warns us that in many cases the causes are not entirely clear.
While the main trigger is usually a serious injury, microinjuries that persist over time can also cause bone marrow edema. During a 10-kilometer race, someone hits the ground about 8,000 times. So this takes its toll on the internal bone structure as well as the muscles and ligaments.
However, movement is not the only trigger. Diseases such as osteoarthritis, avascular necrosis (lack of blood supply), osteoporosis or complex regional pain syndrome also promote the appearance of this inflammation. Basically, anything that weakens the bone makes it more prone to fracture.
The Symptoms of Bone Marrow Edema
The clinical manifestations of bone marrow edema can vary from person to person, depending on the severity with which it occurs. According to information published in the journal Clinical Rheumatology (Spanish link), the main symptoms are the following:
- A localized pain in the affected bone structure.
- Discomfort in putting the injured bone to work. The pain increases during exercise.
- If the injury is not treated immediately, the pain will prolong even when the patient is resting.
- In the most severe cases , people may experience discomfort with daily activities such as walking.
Due to their nature, it is easy to guess that bone marrow edema is more common in the knees, the metatarsals of the foot, or the heel bone. Still, the symptoms vary depending on the bone structure in question.
Diagnosis
This type of lesion is not visible with traditional radiography, so an MRI is necessary. Studies also show that new techniques such as Dual-Energy Computed Tomography (DET), which reconstructs images of the decomposition of materials, can be very useful tools when it comes to detecting bone edema.
What is the treatment for bone marrow edema?
According to traumatology professionals, the treatment of bone edema involves several stages. The phases consist of the advice and treatments listed below:
- Rest is a determining factor for optimal recovery. To relieve acute symptoms, the use of crutches is important. It is also important to reduce stress and strain on the bone for at least four weeks.
- Various medications may also be helpful. Think for example of painkillers to control pain, bisphosphonates, vitamins and other compounds to increase bone density or iloprost for vasodilation.
- After the initial medical stages, it is wise to support recovery with physiotherapy. This can be magnet therapy, thermotherapy, muscle relaxation, water exercises and other techniques.
In the most severe cases, a visit to the operating room may be necessary. It is possible to do a spinal cord decompression using multiple perforations to remove the fluid from the bone.
Precautionary actions
As the popular saying goes, ‘prevention is better than cure’. We should not burden our body more than necessary. In extreme physical activity, the presence of a trainer who monitors our exercises is also essential.
At the same time, if you experience discomfort after walking, running or any other activity, you should see a doctor. Whether it’s bone marrow edema, a fracture or a sprain, you need to get an early diagnosis to intervene in time and prevent complications.